Cases clearly define liability of dog-owners
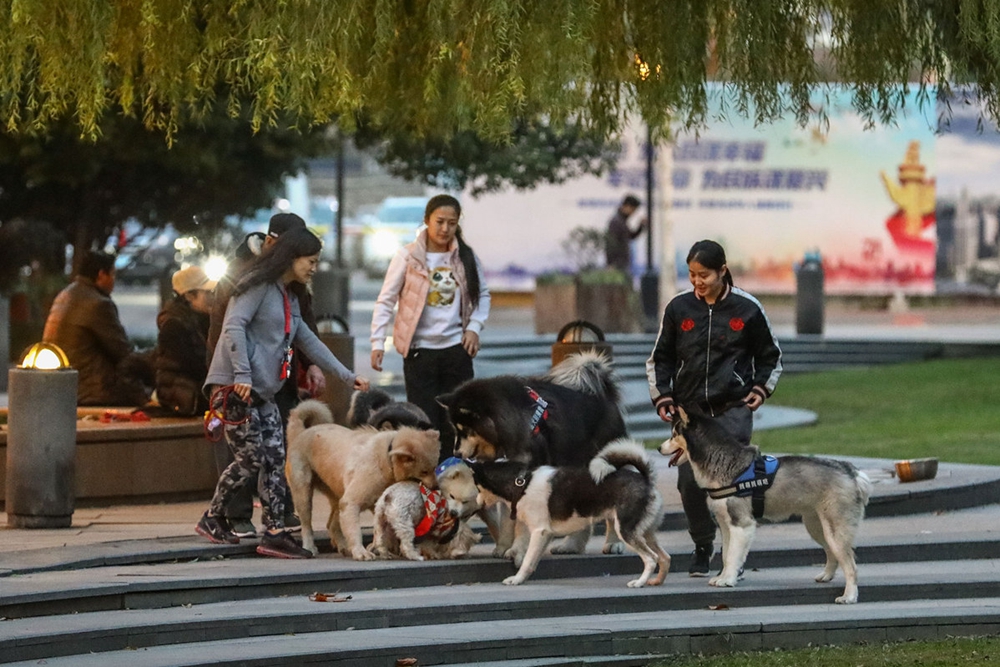

People walk their dogs in a park. [Photo/China Daily]
The supreme court has recently observed that the dog-owners should bear full responsibility if their dogs attack someone.
There are relevant laws and regulations regarding dogs hurting people, stipulating that the dog-owners should bear criminal and administrative legal responsibilities if they are found responsible for not controlling their pets.
Yet the Civil Code stipulates that if it can be proved that there was some intentional fault or negligence on the part of the victims, the dog-owners can be exempted from any responsibility or their culpability reduced. That clause has made it difficult for victims in some cases to protect their rights and interests.
By releasing a series of typical cases, the supreme court has addressed such questions. The key is the reaffirmation of "no-fault liability", under which owners of aggressive dogs must bear full responsibility for any harm done regardless of whether or not the victims were at fault.
This is because aggressive dogs pose a higher risk to society, and those raising such dogs should bear greater responsibility. Further, raising large dogs in downtown areas is against the rules.
The releasing of the cases is conducive to clarifying the legal responsibility of relevant parties and raising the dog-owners' awareness of their responsibilities.